Beginning with the question of whether Merit Pay truly enhances employee performance, this introduction aims to grab the attention of the readers with an intriguing overview of the topic.
Following that, a detailed description will be provided in the subsequent paragraph.
Definition of Merit Pay
Merit pay, also known as pay-for-performance, is a compensation system where employees receive raises or bonuses based on their performance. This differs from traditional pay structures, where pay increases are often based on factors like seniority or cost of living adjustments.
Examples of Merit Pay in Industries
- In the sales industry, employees may receive commissions based on their sales performance.
- In the tech industry, software engineers might receive bonuses based on the successful completion of projects.
- In healthcare, physicians could earn incentives for meeting certain quality care metrics.
Pros and Cons of Merit Pay
When considering implementing a merit pay system in an organization, it is essential to weigh the advantages and potential drawbacks associated with this approach.
Advantages of Merit Pay
- Increased Motivation: Merit pay can incentivize employees to perform at their best in order to receive rewards based on their individual performance.
- Retention of Top Talent: Offering merit-based rewards can help attract and retain high-performing employees who are motivated by the opportunity for increased pay.
- Clear Performance Expectations: Merit pay systems often come with clear performance metrics, which can help employees understand what is expected of them and how they can improve.
- Improved Productivity: By rewarding employees for their individual contributions, merit pay can lead to increased productivity and overall organizational success.
Drawbacks of Merit Pay
- Subjectivity: Evaluating individual performance can be subjective and prone to biases, potentially leading to unfair assessments and demotivation among employees.
- Competition Over Collaboration: Merit pay systems may foster a competitive environment where employees prioritize personal gain over teamwork and collaboration.
- Unintended Consequences: Employees may focus on tasks that are easily measurable and rewarded, neglecting other important aspects of their role that are not directly tied to merit pay.
- Costly Implementation: Implementing and managing a merit pay system can be costly and time-consuming for organizations, especially if not done effectively.
Real-World Examples
In the tech industry, companies like Google and Microsoft have successfully used merit pay to motivate employees. These companies tie bonuses and salary increases to individual performance evaluations, encouraging employees to strive for excellence in their work. Additionally, performance-based bonuses are common in sales-driven organizations like Salesforce, where sales representatives receive commissions based on their sales performance.
Impact on Employee Motivation
Merit pay can have a significant impact on employee motivation and engagement within an organization. By rewarding employees based on their individual performance, merit pay creates a sense of fairness and recognition, motivating employees to work harder and achieve better results.
This can lead to increased productivity, higher job satisfaction, and a more positive work environment overall.
Motivational Effects of Merit Pay
- Merit pay provides a clear link between performance and rewards, giving employees a direct incentive to excel in their roles.
- It can foster healthy competition among employees, pushing them to strive for excellence and continuously improve their performance.
- Merit pay rewards top performers, motivating them to maintain high levels of productivity and quality of work.
- Employees who feel their efforts are recognized and rewarded are more likely to be engaged and committed to their jobs.
Tailoring Merit Pay for Different Employees
- For high achievers, merit pay can serve as a powerful motivator to continue performing at a high level and reach their full potential.
- For average performers, merit pay can provide a goal to work towards and an opportunity to improve their skills and performance to earn higher rewards.
- For low performers, merit pay can act as a wake-up call to identify areas for improvement and strive for better results in order to earn higher compensation.
- Managers can customize merit pay programs to align with individual employee goals, preferences, and motivations, maximizing the impact on employee engagement and performance.
Effectiveness in Improving Performance
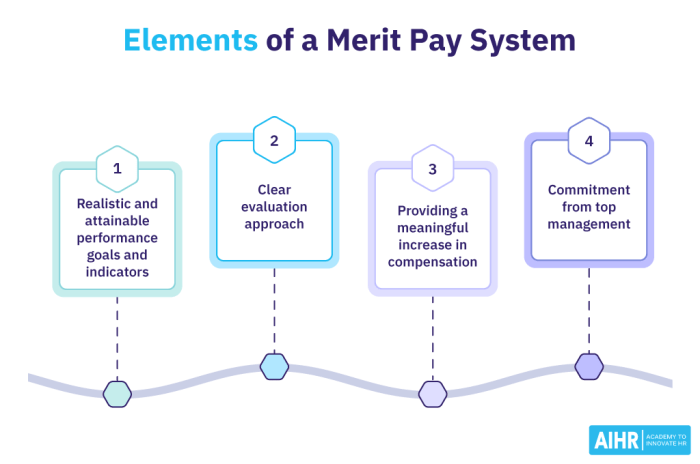
When it comes to the effectiveness of merit pay in improving employee performance, various studies and research have been conducted to analyze the correlation between the two. These findings shed light on factors that can either enhance or hinder the impact of merit pay on performance outcomes.
Research Findings on Merit Pay and Performance
Studies have shown that there is a positive relationship between merit pay and employee performance
Factors Influencing the Effectiveness of Merit Pay
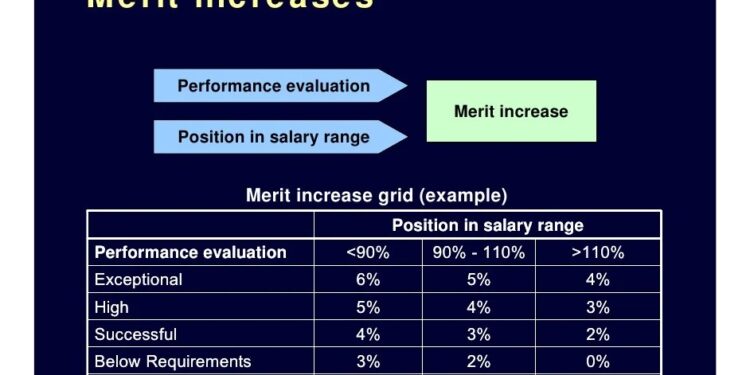
- Clear Performance Metrics: Establishing clear and measurable performance metrics is crucial for the success of a merit pay system. Employees need to understand what is expected of them in order to be motivated to reach those goals.
- Regular Feedback: Providing regular feedback to employees on their performance can help them track their progress and make necessary adjustments to improve. This feedback loop is essential for the effectiveness of merit pay.
- Equitable Reward Distribution: Ensuring that merit pay rewards are distributed fairly based on performance outcomes is key to maintaining employee morale and motivation. Transparency in the reward system is essential.
Best Practices for Implementing Merit Pay Systems
- Set Clear Objectives: Clearly define the objectives of the merit pay system and communicate them effectively to employees.
- Train Managers: Provide training to managers on how to effectively evaluate employee performance and administer merit pay rewards.
- Monitor and Adjust: Continuously monitor the effectiveness of the merit pay system and make adjustments as needed to optimize performance outcomes.
Considerations for Implementation
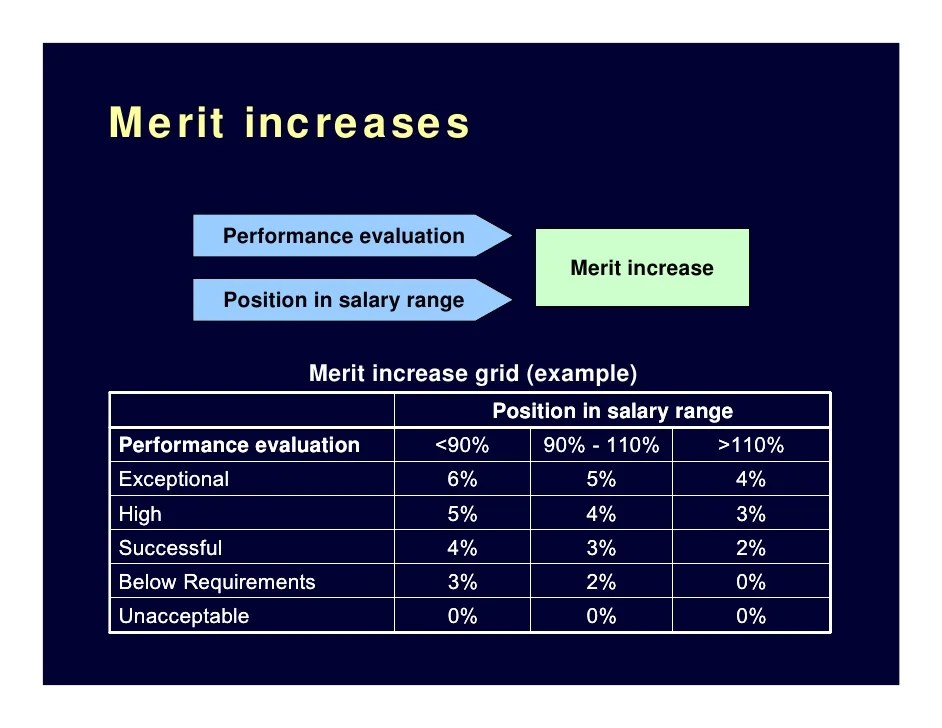
Implementing a merit pay system in an organization requires careful planning and consideration. It is essential to take into account various factors to ensure the success of the program and maximize its effectiveness.
Key Considerations for Implementation
- Clearly Define Performance Metrics: Organizations must establish clear and objective performance metrics that employees understand and can strive to achieve. This ensures that merit pay is awarded based on measurable outcomes.
- Transparency and Fairness: It is crucial to maintain transparency and fairness throughout the merit pay process. Employees should understand how their performance is evaluated and how merit pay decisions are made to avoid any perceptions of bias.
- Training and Development: Providing opportunities for training and development can help employees improve their skills and performance, ultimately leading to better outcomes for the organization. Investing in employee growth is key to the success of a merit pay system.
Strategies for Communicating Merit Pay Structures to Employees
- Hold Information Sessions: Organize sessions to explain the merit pay system, how performance will be evaluated, and how merit pay decisions will be made. This helps employees understand the process and align their goals accordingly.
- Provide Written Materials: Distribute written materials outlining the merit pay structure, performance metrics, and timelines. This allows employees to refer back to the information and clarifies any potential questions or concerns.
- Offer Individual Meetings: Schedule one-on-one meetings with employees to discuss their performance, goals, and how they can improve to be eligible for merit pay. Personalized feedback can motivate employees to strive for excellence.
Evaluating the Success of a Merit Pay Program and Making Adjustments
- Monitor Performance Metrics: Regularly track performance metrics to assess the impact of the merit pay program on employee performance. Analyze data to identify trends, areas of improvement, and top performers deserving of merit pay.
- Solicit Feedback: Gather feedback from employees about their experience with the merit pay system. Use surveys or focus groups to understand their perspectives, identify challenges, and make necessary adjustments for future implementations.
- Review and Adjust Criteria: Periodically review the performance metrics and criteria used for merit pay evaluations. Modify them as needed to align with changing organizational goals and ensure the effectiveness of the program.
Summary
Concluding with a captivating summary of the discussion, this final paragraph wraps up the key points and leaves a lasting impression on the readers.
Answers to Common Questions
Does Merit Pay guarantee better performance from employees?
Merit Pay can serve as a motivator for employees to strive for better performance, but it's not a guarantee as individual factors and circumstances play a role.
How can companies effectively communicate a merit pay system to employees?
Companies should ensure clear and transparent communication about the criteria, process, and outcomes of the merit pay system to avoid misunderstandings.
What are some common challenges associated with implementing a merit pay system?
Challenges may include defining merit criteria objectively, dealing with employee perceptions of fairness, and managing expectations around performance evaluations.
Is merit pay more effective than traditional pay structures in motivating employees?
Merit pay has shown to be effective in motivating employees as it rewards individual performance, but its effectiveness can vary based on organizational culture and context.